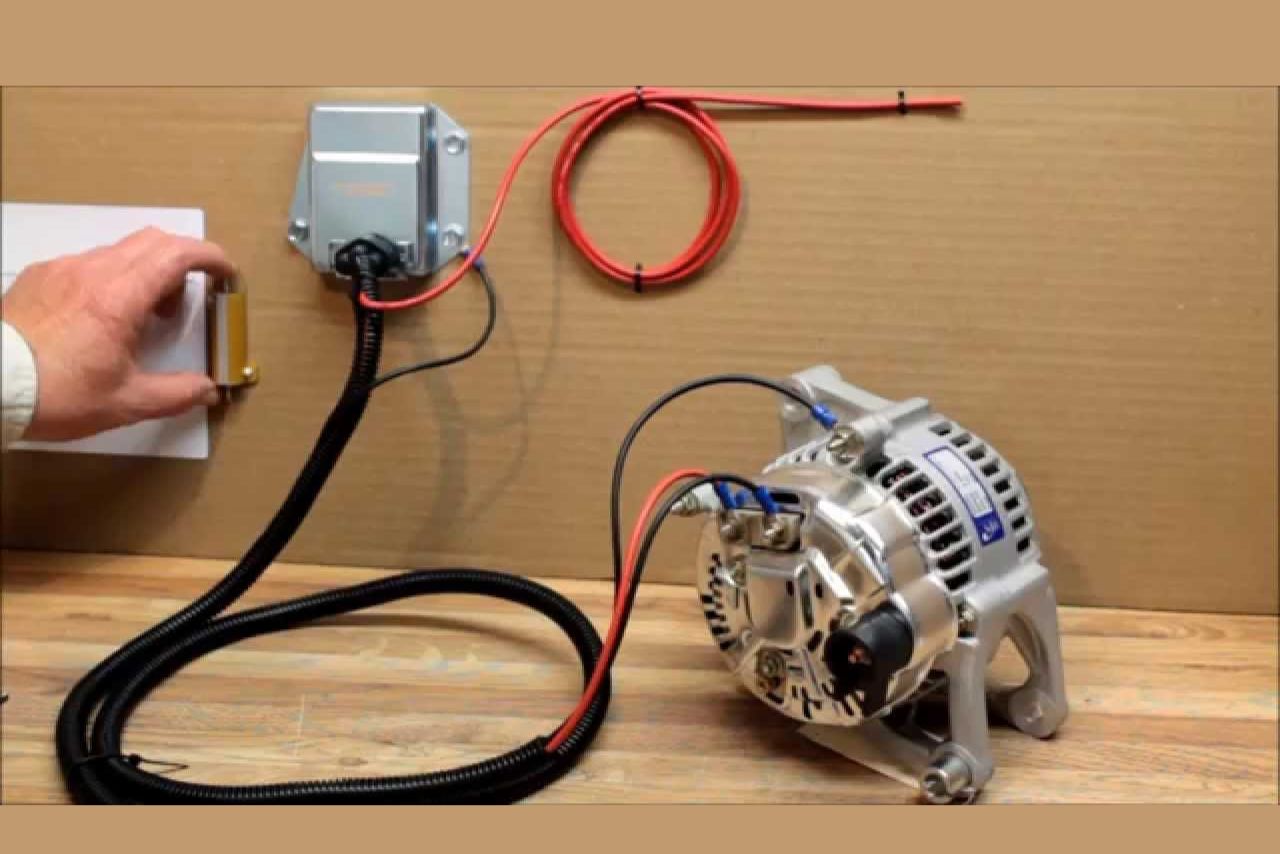
Are you experiencing issues with the voltage regulator on your alternator? If so, you may be wondering if it’s possible to bypass the voltage regulator altogether.
In this article, we will explore the topic of How to Bypass Voltage Regulator on an Alternator and provide you with some helpful information and tips.
The voltage regulator plays a crucial role in regulating the electrical output of your alternator. It ensures that the voltage remains at a stable level to prevent damage to your vehicle’s electrical system.
To bypass a voltage regulator on an alternator, you need to disconnect the voltage regulator connector and connect a jumper wire between the “A” and “F” terminals of the connector. This will bypass the regulator and allow the alternator to operate at full output.
It is important to note that bypassing the voltage regulator can damage your battery and other electrical components, so it should only be done as a temporary measure.
That being said, here, we will discuss some steps you can take to bypass the voltage regulator if you find yourself in a situation where it’s necessary.
Understanding the Purpose of a Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator plays a crucial role in the functioning of an alternator. It ensures that the electrical system in a vehicle receives a steady and controlled supply of voltage.
Here’s a breakdown of its purpose and how it works:
The voltage regulator is a vital component in the alternator system of a vehicle.
It maintains a stable voltage output, prevents overcharging of the battery, compensates for varying electrical loads, and protects sensitive electronic components.
Identifying Signs of a Faulty Voltage Regulator

If you suspect that your alternator’s voltage regulator is faulty, there are several signs you can look out for.
Here, we will discuss these indicators to help you identify whether your voltage regulator needs attention.
1. Dim or Flickering Lights
One of the most common signs of a faulty voltage regulator is dim or flickering lights.
If you notice that the headlights, dashboard lights, or interior lights are not as bright as they used to be, or they flicker while driving, it could be a sign that the voltage regulator is not effectively regulating the electrical output.
2. Battery Problems
A faulty voltage regulator can also lead to battery-related issues. Keep an eye out for:
3. Electrical System Malfunctions
When the voltage regulator is not functioning correctly, it can affect various electrical components in your vehicle. Look out for these symptoms:
4. Burning Smell or Smoke
A burning smell or smoke coming from the alternator can indicate a serious issue with the voltage regulator or other electrical components.
If you detect these odors, it is essential to address the problem immediately and seek professional assistance.
Remember, these signs are not exclusive to a faulty voltage regulator, and other factors can contribute to similar symptoms.
If you suspect an issue, it is always recommended to consult a qualified mechanic or technician for a thorough diagnosis and proper repair.
Tools and Materials Needed for Bypassing the Voltage Regulator
When it comes to bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator, there are a few tools and materials you’ll need to have on hand.
This section will guide you through the essential items required for the job. So, let’s get started!
1. Multimeter
A multimeter is an indispensable tool for any electrical work, including bypassing the voltage regulator.
It helps you measure voltage, current, and resistance, enabling you to diagnose problems and ensure the bypass is successful.
Make sure you have a reliable multimeter before diving into the task.
2. Wire Cutters and Strippers
To perform the bypass, you’ll need to cut and strip wires, so having a reliable pair of wire cutters and strippers is crucial.
These tools will make the process easier and ensure clean cuts and accurate stripping for a secure connection.
3. Electrical Tape or Heat Shrink Tubing
After making the necessary wire connections, it’s essential to insulate them properly to prevent any short circuits or electrical mishaps.
You can use electrical tape or heat shrink tubing to cover the exposed wires and provide insulation. Choose whichever option suits your preferences and ensures electrical safety.
4. Wire Connectors
Wire connectors are essential for joining wires securely and maintaining electrical continuity.
Depending on the type of wires you’re working with, you may need butt connectors, spade connectors, or ring connectors.
Ensure you have a variety of wire connectors on hand to accommodate different wire sizes and types.
5. Socket Set
In some cases, you may need to remove the alternator from the vehicle to access the voltage regulator.
Having a socket set with the appropriate sizes will allow you to remove and reinstall the alternator efficiently.
6. Step-by-Step Guide or Online Resources
Lastly, don’t forget to have a reliable step-by-step guide or access to online resources that explain the bypassing process.
These resources will provide you with the necessary instructions, precautions, and troubleshooting tips to ensure a successful bypass.
By gathering these tools and materials before starting the voltage regulator bypass, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle the task with confidence.
Remember to follow proper safety protocols and consult professional advice if needed. Good luck with your alternator modification!
Step-by-Step Guide to Bypassing the Voltage Regulator
In this section, we will guide you through the process of bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator.

Bypassing the voltage regulator can be useful in certain situations, such as when you need to test the alternator or if the voltage regulator is faulty. Here are the steps you can follow:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Disconnect the battery |
| 2 | Locate the voltage regulator |
| 3 | Identify the connections |
| 4 | Disconnect the connections |
| 5 | Connect the field terminal to the battery terminal |
| 6 | Reconnect the battery |
It’s worth mentioning that bypassing the voltage regulator should only be done temporarily and for specific purposes.
That’s it! You have successfully bypassed the voltage regulator on your alternator. Remember to exercise caution and consult a professional if you encounter any difficulties or uncertainties during the process.
Testing the Alternator After Bypassing the Voltage Regulator
After successfully bypassing the voltage regulator on your alternator, it’s important to test the alternator to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
This will help you confirm that the voltage regulator was indeed the issue and that your bypass has been successful. Here are a few steps you can follow to test your alternator:
Remember, testing the alternator after bypassing the voltage regulator is crucial to ensure that your electrical system is functioning properly.
Watch video: How to Bypass Voltage Regulator on an Alternator
Last Talk: How to Bypass Voltage Regulator on an Alternator?
Bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator can be a temporary solution in certain situations.
However, it is important to note that this should only be done if absolutely necessary and with caution. Here are a few key points to remember:
| Key Takeaways |
|---|
| Bypassing the voltage regulator is a temporary solution. |
| It can potentially cause overcharging and damage to the electrical system. |
| Technical knowledge and expertise are required. |
| Bypassing the regulator may void warranties. |
| Regular maintenance and inspection are important. |
In summary, while bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator can be a temporary solution, it is not recommended unless absolutely necessary.
It is always best to consult a professional or seek expert advice to ensure the safety and longevity of your vehicle’s electrical system.
FAQs
How do I bypass a voltage regulator on an alternator?
To bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator, you must first disconnect the regulator from the alternator. Then, connect the output terminal of the alternator directly to the battery.
This will bypass the voltage regulator and allow the alternator to operate at full capacity.
What are the risks of bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator?
Bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator can lead to increased wear and tear on the alternator due to overcharging the battery.
It can also lead to damage to the vehicle’s electrical system due to overcharging if the alternator is not powerful enough to handle the increased current.
What should I do before bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator?
Before bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator, you should ensure that the alternator is powerful enough to handle the increased current.
You should also make sure that the battery is rated to handle the increased current.
Is bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator a permanent solution?
No, bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator is not a permanent solution. The regulator should be reconnected after the alternator has been tested for proper operation.
If the alternator does not operate properly, the regulator should be replaced.
Is bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator a difficult task?
No, bypassing a voltage regulator on an alternator is not a difficult task. It is a relatively simple process that requires only basic electrical knowledge and tools.
However, it is important to take the necessary safety precautions before making any connections.